Navmesh in Unity
Navigation is a crucial aspect of game development, especially when creating AI-controlled characters that need to move intelligently through your game world. In order to allow them to move around our level, we need to use NavMesh.
NavMesh, short for Navigation Mesh, is a data structure that represents the walkable surfaces in your game environment. Think of it as an invisible map that tells AI agents where they can and cannot go. The NavMesh system analyzes your scene’s geometry and creates a simplified mesh that defines navigable areas, automatically handling obstacles and different terrain types.
How to set up NavMesh in Unity?
Getting started with NavMesh is straightforward. First, you need to mark your surfaces as static by selecting your ground objects and checking “Navigation Static” in the Inspector. Then, open the Navigation window (Window > AI > Navigation) and click “Bake” to generate your NavMesh. Unity will process your scene and create the navigation mesh based on the settings you provide.
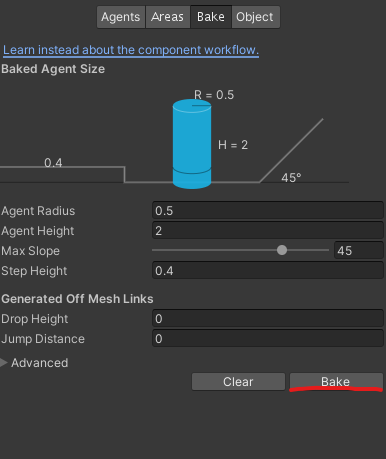
The baking process itself considers several parameters that you can modify. The Agent Radius determines how close AI can get to walls and obstacles, while Agent Height ensures characters won’t try to walk through low ceilings. Max Slope defines the steepest angle your agents can climb, and Step Height controls the maximum obstacle height they can step over.
How to use NavMesh Agents?
Once your NavMesh is baked, you need to add a NavMesh Agent component to any character you want to navigate. This component handles all the pathfinding calculations and movement automatically. Simply set a destination using the SetDestination method, and the agent will find the optimal path and move there.
You can customize agent behavior through various properties. Speed controls how fast the agent moves, while Angular Speed determines how quickly it can turn. Acceleration and Stopping Distance fine-tune the movement to feel more natural and responsive. The agent also handles dynamic obstacle avoidance, automatically adjusting its path when other agents or obstacles block the way.
While NavMesh is efficient, it’s important to consider performance, especially in large or complex scenes. Baking a NavMesh can be time-consuming for big environments, so consider using runtime NavMesh building only when necessary. The NavMesh system is optimized for static environments, so frequent rebaking during gameplay can impact performance.
NavMesh excels in many scenarios. It’s perfect for enemy AI that needs to chase players through complex levels, NPC characters that wander through towns and buildings, or RTS-style games where units need to navigate around obstacles and other units. The system handles most pathfinding challenges automatically, letting you focus on higher-level AI behavior and game logic.